Potential Sources of Disease Spread
According to the National Institute of Health, beauty salons are considered a major health concern.
Salons provide a wide range of services including hairdressing, nail care (manicures and pedicures), hair removal by waxing and threading, mud baths, and many other services, some of which require the use of cosmetics, most of which are chemical compounds derived from natural or synthetic sources.
The Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, defines cosmetics as:
Intended to be applied to the human body for cleansing, beautifying, promoting attractiveness, or altering the appearance without affecting the body’s structure or functions.

The health risks associated with beauty salons vary depending on the products and tools used, the nature of the business, and the service providers themselves. Salons can contribute to and cause the spread of viral, fungal, and bacterial infections if precautions re not taken, or if industry standards are not followed.
Salons tend to use chemical and physical methods to sterilize and disinfect tools and equipment. Autoclaving is the most reliable way to kill all microbes, but in general it cannot be used for sterilizing electrical equipment, and autoclaving requires a long time.

Salons mostly use chemical disinfectants, which are effective in killing microbes or at least slowing their growth. Many of these chemicals are hazardous and they must be used carefully and following all instructions and procedures on the labels and accompanying literature.
After cleaning and sterilizing, the tools must be stored properly in a cool and dry place to reduce the risk of any growth of bacteria and fungi remaining on tools and therefore, the spread of disease.
Several literature reports document the existence of a variety of microorganisms isolated from beauty tools used in salons such as nail care tools, and sharpeners. All samples contained pathogenic bacteria, including species of Staphylococcus, (a type of bacteria with more than 30 types, and its most common infection is skin infection), Bacillus, (A bacteria that causes gastroenteritis) and Streptococcus, (Streptococcus is best known for causing strep throat), and pathogenic fungi, including Aspergillus, (A type of mold that can cause lung infections to people with weak immune systems), Trichophyton, (This bacteria causes tinea, the best known is athlete’s foot, but tinea is a dermatologic condition that can affect the head, beard, hands, etc.), Microsporum, (Another type of bacteria that causes tinus) Malassezia, and Mucor (These last two were also measured, but are less infectious). The highest microbial content in this study was measured on clippers, as these tools received the lowest level of sterilization practice among all of the tested tools.
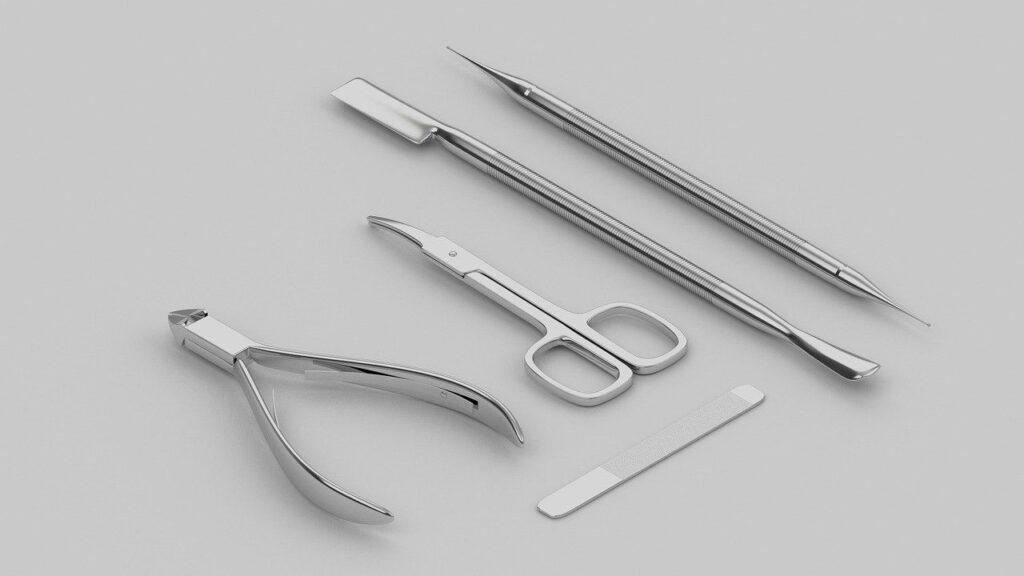
A review of several studies showed that more bacterial species were isolated from cosmetic products in beauty salons. The main reason for this is likely due to the preservative used in cosmetic products being more effective in inhibiting fungal growth than bacterial growth.
Some microbes isolated from cosmetic products and tools are considered as significant threats to public health. Bacteria related to nosocomial infection microbes are rarely and poorly controlled by antibiotics. In addition to infections acquired from hospitals, food-borne diseases are another issue caused by microbes found on salon instruments and products.
There is a need to increase the public’s awareness of the potential for disease transmission through the common tools and products used in beauty salons.
In terms of awareness, the International Organization for Standardization provided guidelines that should be taken into account in the field of cosmetic manufacturing, from manufacturing to the usage by customers, until waste disposal.
